What Is Music Production?
The process of recording or making a music product in a recording studio from which a master may be made is known as music production. After then, the music product may be used in a variety of ways, including as CDs, mp3 downloads, commercials, movies, computer games, and so on.
What is a Recording Studio?
In most cases, a recording studio consists of two rooms. The main chamber is known as “the control room,” while the second room is known as “Live room.” These rooms are soundproofed to ensure that no outside noise gets into the studio and vice versa. Sound does not transfer between the booth and the control room since it is acoustically separated.
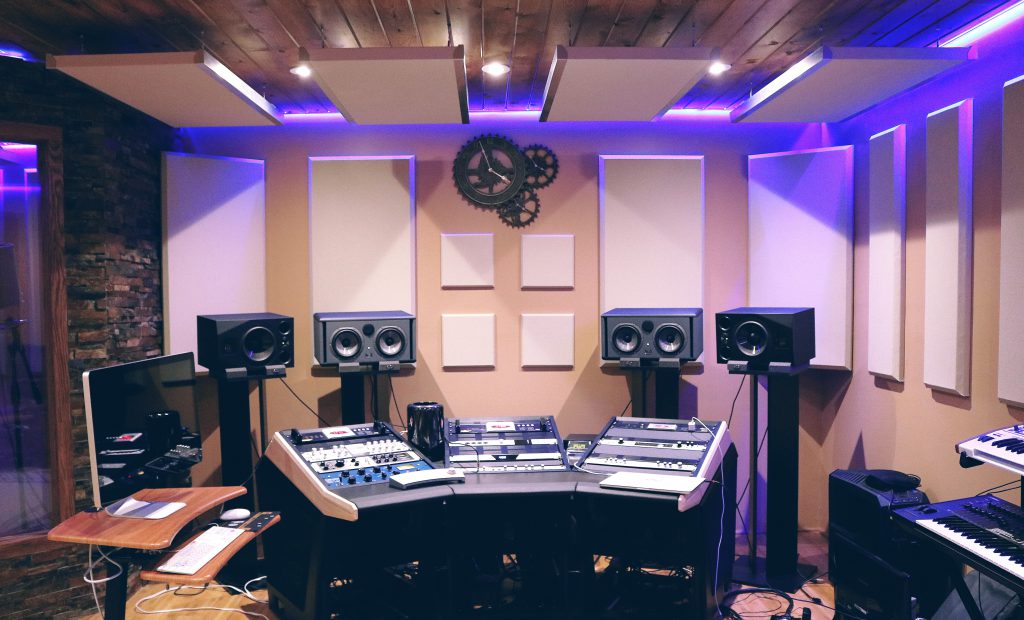

The control room :- rooms all of the recording equipment as well as the majority of the gear. The sound engineer and music producer frequently sit here while listening to the recording through loudspeakers.
Live Room :- The musicians or vocalists execute their takes into microphones that deliver the signal to the control room. In order for the music they are performing to not seep through into the microphone, musicians and vocalists usually wear headphones in the booth. Previously, musicians would all perform at the same time and be recorded in a single take. That’s why previous studios were so large to accommodate so many artists performing at once. Most producers nowadays record one performer at a time, using many takes and multitrack recording. These days, it’s very uncommon for a booth to be quite small, just big enough for two or three individuals at most.
- What Equipment Do I Require?
So, a Modern digital home recording studio may have all of the following components:
▪ A Computer
▪ Daw (Digital Audio Workstation) Software Package
▪ Audio Interface / Soundcard
▪ Microphone
▪ Studio Monitor
▪ Midi Controller
▪ Mic Stand And Cables
1. Computer
Your operation’s mothership will be here. On this machine, all sequencing, programming, and recording will be completed, modified, and stored.
*NB* My recommendation is to obtain the fastest computer you can because working with audio on a computer may be highly taxing on the CPU (central processing unit), especially if you’re running a virtual studio with all instruments and effects created by the machine’s own CPU.
2. DAW (Digital Audio Workstation)
This will be your primary piece of software. The DAW functions as a sequencer, multitrack recorder, reverbs, compressors, mixer, editor, and mastering tool.
*Note: I use Logic Studio myself. If you haven’t used a DAW before, I highly recommend Logic Studio. It’s essentially a studio in a box. All of my future music production tutorials will be done in Logic Studio. You may, however, use any respectable DAW because the majority of what I’m teaching are concepts and principles that can be simply transferred to any DAW.
3. Audio Interface/ Soundcard
The audio interface is the link between the analogue and digital worlds. When you record into the computer using the audio interface, all of your audio from microphones, guitars, and any other sound moving through an analogue wire will be transformed from analogue to digital. When you play back your recordings, the computer converts them from digital to analogue.

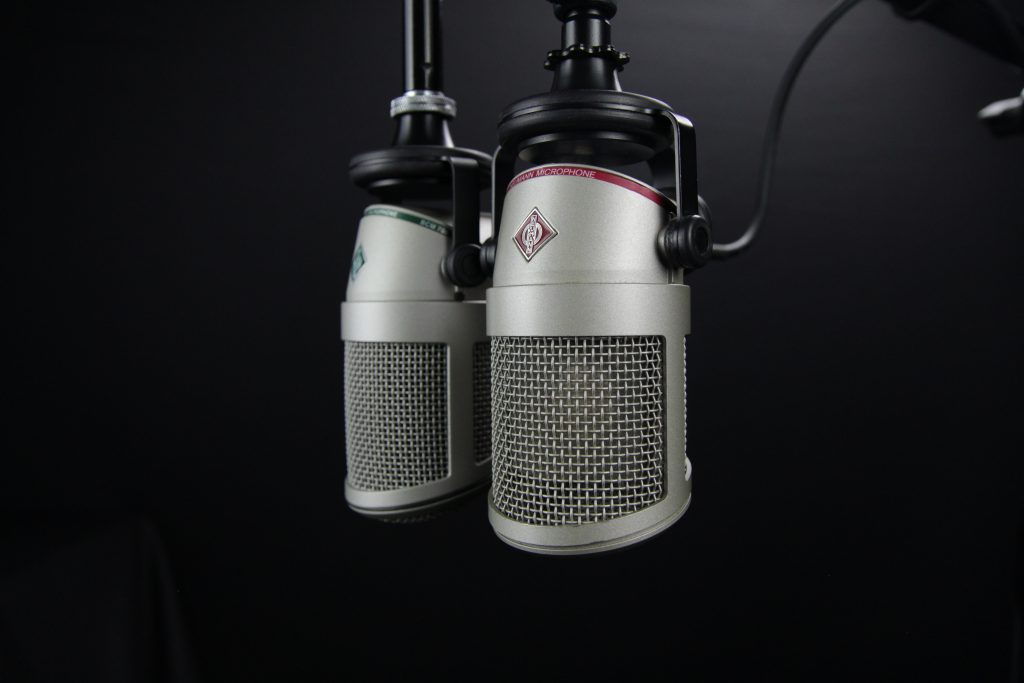
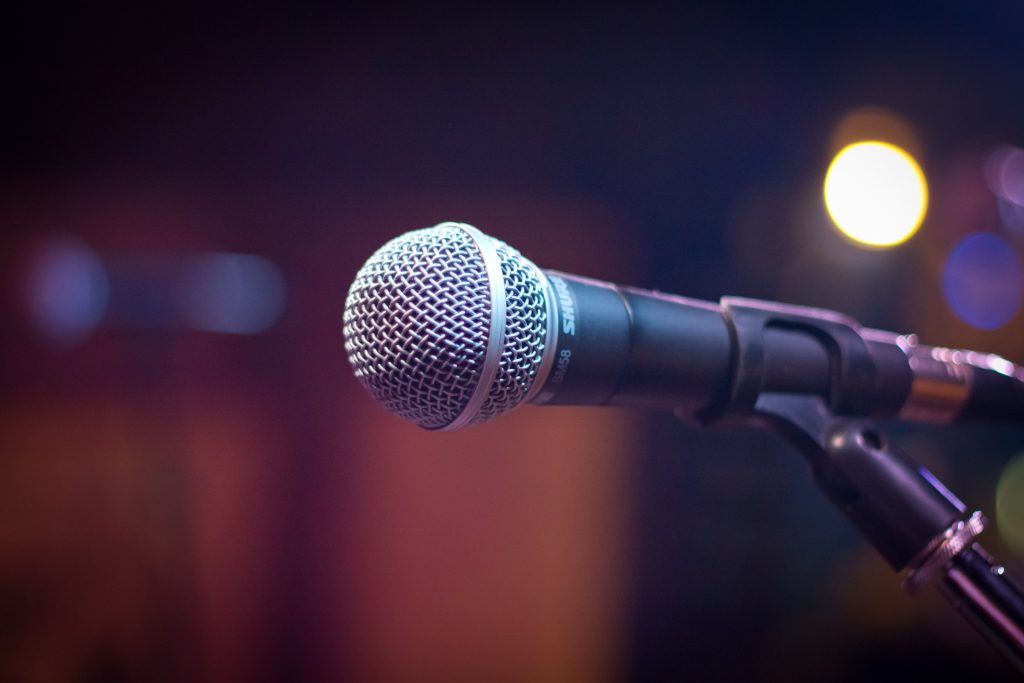
4. Microphone
Microphones pick up sound waves in the air and convert them to electrical impulses that are similar. You may also transfer the signals from the mic’s output to a mixer or audio interface for recording, or to a speaker, which converts them back into sound waves, to duplicate the original sounds.
Types of Microphones
1. Dynamic Microphone
2. Condenser Microphone


5. Studio Monitors
Your music will be heard through the amplifier and speakers (monitors). The sound will be digitally output from the computer to the sound card (Audio Interface) and analoguely output from the sound card to the amplifier and speakers.
*Note: I recommend going with self-powered Nearfield monitors. Self-powered speakers are easy to use, and the manufacturer has carefully matched the amp to the speaker. Nearfield monitors are a type of monitor that is designed to allow you to hear bass sounds clearly from a short distance ( i.e. in a studio). This is critical.
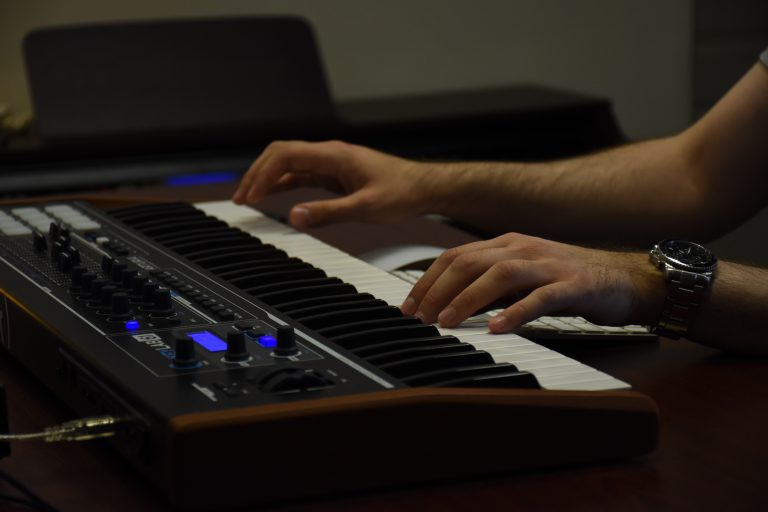
6. MIDI Controller
A controller is required in every studio to enter the notes or beats that you want into your song. The majority of producers utilize a keyboard controller, however guitar controllers are also available. Originally, all controllers were MIDI-based, but nowadays, the majority of controllers are USB-based.
*NB* If you’re intending to work with a laptop as your primary computer, I recommend getting a USB controller. If you pick a MIDI controller, you will also need a MIDI interface to connect it to.

7. Mic Stand and Cables
A controller is required in every studio to enter the notes or beats that you want into your song. The majority of producers utilize a keyboard controller, however guitar controllers are also available. Originally, all controllers were MIDI-based, but nowadays, the majority of controllers are USB-based.
*NB* If you’re intending to work with a laptop as your primary computer, I recommend getting a USB controller. If you pick a MIDI controller, you will also need a MIDI interface to connect it to.